Introduction
The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than their surrounding rural areas. This temperature difference is mainly caused by human activities and the built environment in cities, which absorb and retain more heat.
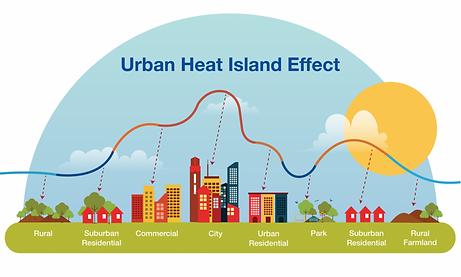
Key Causes of UHI:
-
Concrete, asphalt, and buildings absorb and store heat during the day and release it slowly at night.
-
Lack of vegetation and green spaces reduces natural cooling from shade and evapotranspiration.
-
Waste heat from vehicles, industries, air conditioning, and other energy uses adds to local warming.
-
Dense infrastructure reduces airflow, trapping heat in built-up areas
Although the Great Appalachian Valley is primarily a natural and rural region, it intersects several urban areas, located within or near valleys. This region is facing UHI in recent years because of following reasons:
-
Topography and Airflow: Valleys can trap warm air and limit ventilation, intensifying the UHI effect in urban areas located within them.
-
Urban Development in Valleys: Cities located in flatter, more accessible valley terrain often experience denser urbanization, increasing impervious surfaces (concrete, asphalt) and retaining more heat.
-
Vegetation & Forested Slopes: The surrounding mountains are often forested, which cool the surrounding rural areas, increasing the contrast in temperature with the urban valleys—magnifying the apparent UHI effect.

